
Topology is the shape of a network.
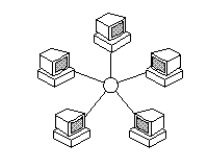 There is a central device to which all the workstations or nodes are
directly connected. The central device is a server or a hub, nodes
communicate across the network by passing data through the hub. The main advantage of a star network is that
one faulty node doesn't affect the rest of the network, and it's easy to add and remove nodes. The main
disadvantage of star networks is that they require more cabling than other topologies which makes them more
expensive. However, communication is fast because there is a direct path from the server to each terminal.
There is a central device to which all the workstations or nodes are
directly connected. The central device is a server or a hub, nodes
communicate across the network by passing data through the hub. The main advantage of a star network is that
one faulty node doesn't affect the rest of the network, and it's easy to add and remove nodes. The main
disadvantage of star networks is that they require more cabling than other topologies which makes them more
expensive. However, communication is fast because there is a direct path from the server to each terminal.
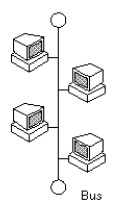 Each workstation is connected to a main cable called a bus or backbone.
Each device has equal status; the advantage is that if one terminal is not working correctly, the others
are not affected. This type of network is very cheap and reliable.
Each workstation is connected to a main cable called a bus or backbone.
Each device has equal status; the advantage is that if one terminal is not working correctly, the others
are not affected. This type of network is very cheap and reliable.
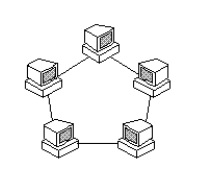 All devices are connected to one another in the shape of a closed loop, so that each device is connected
directly to two other devices, one on either side of it. All devices are equal, the disadvantage – if there
is a fault in any part of the circle, all the nodes are affected.
All devices are connected to one another in the shape of a closed loop, so that each device is connected
directly to two other devices, one on either side of it. All devices are equal, the disadvantage – if there
is a fault in any part of the circle, all the nodes are affected.
 Devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes. In a true mesh topology
every node has a connection to every other node in the network.
Devices are connected with many redundant interconnections between network nodes. In a true mesh topology
every node has a connection to every other node in the network.
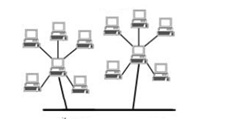 Is a hybrid topology. Groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone.
Is a hybrid topology. Groups of star-configured networks are connected to a linear bus backbone.